|
One of the best ways to fully understand the concept of nationalism is to view its progress chronologically. Here, for example, the evolution of nationalism has been laid out on a timeline, beginning with its first real victory in the American Revolution, and carrying on to modern times.
So scroll on down and take a journey, from Metternich to MacDonald, from Hitler to Haider, heeeeeeeeere's Nationalism!

|
| The British soldiers were nicknamed the Redcoats, although we'll never fully understand why... |
1776- America declares its independence from Great Britain with the signing of the Declaration of Independence in Philadelphia
1783- The American War of Independence draws to a close; the United States have won their freedom from British oppression
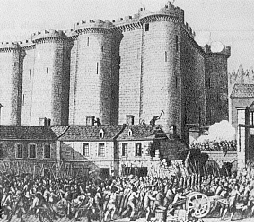
|
| Most agree that the Storming of the Bastille is what finally Bas-stole victory from the King's grasp |
1789- The first French Revolution is launched
1793- Reign of Terror, Louis XVI & Georges Danton executed by Jacobin leader Maximilian Robespierre
1794- Robespierre executed by way of the guillotine
1795- The Director takes control of the French republic
1798- Napoleon's Egyptian Campaign
1799- Consulate established; Napoleon stages coup d'etat, proclaiming himself First Consul
1803- The United States of America purchases the Louisiana Territory from Napoleon's France

|
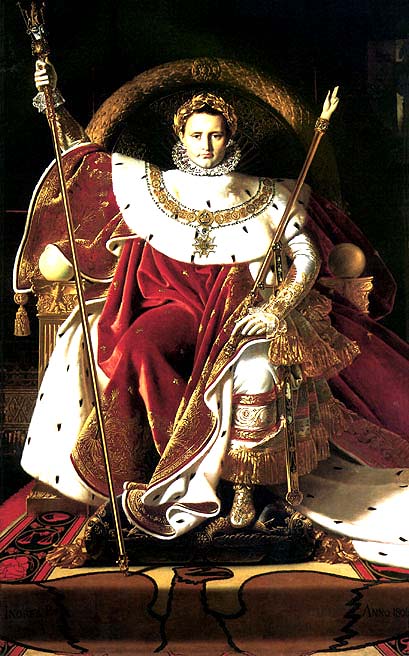
| By proclaiming himself Emperor, Bonaparte ensured that he wouldn't Be-aparte from power for a while. |
1804- Napoleon, by way of a Plebiscite, becomes Emperor of France; the Napoleonic Code was implemented
1806- The German people get their first taste of unity when the Confederation of the Rhine is established, under Napoleonic control
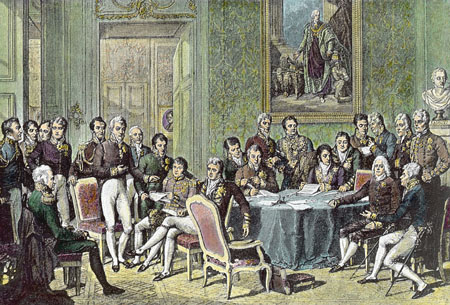
|
| The Congress of Vienna attempted to balance power in Europe. But Napoleon would have none of that. |
1814- Napoleon forced to abdicate (and is subsequently exiled to the Mediterranean Island of Elba), the Bourbon Dynasty is reinstated in France, Louis XVIII is proclaimed King; Metternich initiates the Congress of Vienna
1815- Congress of Vienna interrupted by Napoleon's 100 Days, Bonaparte is defeated by Wellington at Waterloo and exiled once more, this time to the Atlantic island of St. Helena, from which there would be no escape; as a result, European powers bring down harsh new regulations on France; the Quadruple Alliance is formed at the Congress of Vienna, joining Great Britain, Austria, Prussia, and Russia together to combat nationalist uprisings
1817- Simon Bolivar becomes first President of Gran Columbia in South America
1818- Thanks to Talleyrand, France is allowed to join the Quadruple Alliance
1819- Carlsbad Decrees: Metternich cracks down on nationalism (largely due to the recent activism in Germany at the Hambach Festival)
1820- Congress of Troppau held; Troppau Protocol calls for all European powers to bind together to stop any nationalist revolts; meanwhile, on the opposite side of the globe, Jose de San Marin proclaims Peru's independence
1821- Congress of Laibach held; basically continued on the ideas discussed in Troppau, and allowed the Austrians to crush the rebellion in Piedmont; Russia, Prussia, and Austria were all pro-intervention concerning revolutionary uprisings, whereas France and Britain took a more liberal stance
1822- Congress of Verona held; discussion held over whether to intervene in the Greek revolt against their Ottoman rulers; every major power had a reason to want the Ottoman empire to fall, but nobody wanted to allowe the other nations to get anything profitable out of the arrangement, so no agreement could be reached, and Greece was left to fend for itself; in the Western Hemisphere, Brazil gains its independence from Portugal
1823- United States of America proclaims the Monroe Doctrine (named after President Monroe, and only received this title some 20 years after his death), which states that no European power shall attempt to reassert its power in the Western Hemisphere, lest it find itself at war with America
1825- Decembrist Revolt in Russia; wealthy liberals attempt to prevent reactionary Nicholas I from becoming Czar; the rebellion is swiftly crushed
1829- The Greeks, after failing in the early 1820s to secede from the Ottoman empire, attempt a revolution again; this time, they have the support of Britain, France, and Russia; an independent Greek state emerges
1830- The July Days occur in France, ultra-royalist Charles X flees to England and liberal Louis-Phillipe, the black sheep of the Bourbons, is crowned King; a Belgian state is created out of part of the Netherlands
1832- Giuseppe Mazzini forms Young Italy

|
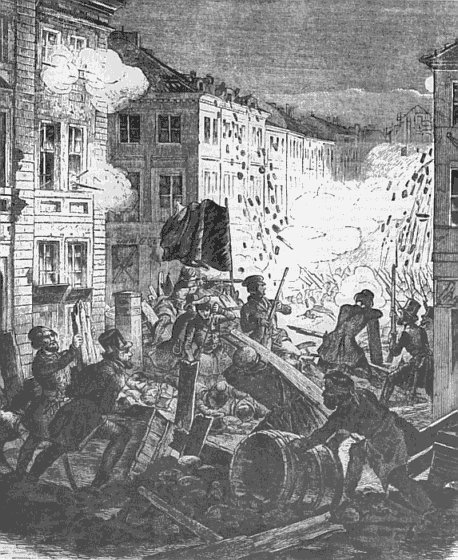
| In 1848, a revolutionary domino effect spread throughout Europe; blockades were set up in cities. |
1848- Socialist riots break out in Europe's major capitols (there an extremely large amount of information on this year in history, therefore it has been broken up into seperate points)
1848 in France- Louis Phillipe abdicates from the throne; the 2nd Republic is established under the Lamartine government; Louis Napoleon is granted power when he is elected President
1848 in Austria- In Vienna, news of the new revolts in Paris prompt workers and students to rise up against the government; Metternich flees to England; provoked by the radical ideals of Lajos Kossuth, Hungary proclaims itself constitutionally independent from the Hapsburg Empire; Emperor Ferdinand grants the same constitutional independence to Bohemia, and fears that the Austrian Empire is collapsing; Austria is driven out of Northern Italy, and the Kingdom of Sardinia declares war on the Hapsburgs
1848 in Prussia- Riots in the streets of Berlin cause the King of Prussia to promise a constitution

|
| The Crimean War's Florence Nightingale: The First Female War-Time Nurse. And look how happy she is! |
1853- Louis Napoleon Bonaparte, previously elected President by France's new democracy, proclaims himself Emperor Napoleon III
1853-56- The Crimean War. Ostensibly, this war was about the rights of Orthodox Christians within the borders of the Ottoman Empire; the Russians favoured the Orthodoxy, while France supported the Roman Catholic population; when the Ottoman Sultan sided with the Roman Catholics, Czar Nicholas I moved his troops closer to the Wallachian and Moldavian border...
1853-56- The Crimean War, Part 2. However, the true purpose of this war was not of religious origin, rather, it was over control of the Dardanelles and Bosporus straits, which connect the Mediterranean Sea to the Black Sea, and are valuable for both trade and military purposes; Russia attempted to forcefully capture the straits (and the surrounding Balkan states, also Turkey); the British and French didn't want Russia to get too powerful, so they came to the Ottoman's aid...
1853-56- The Crimean War, Part 3. After Austrian and Prussian neutrality, the Russians were defeated and lost control of the Danube delta. The Black Sea became neutral territory (neither Russia, nor Austria, nor the Ottomans were allowed to have warships on the sea)
1853-56- The Crimean War, Part 4: The Aftermath. Sardinia, Cavour especially, sensing Austria's weakness, gathered support for a unified Italian state; the Ottomans' weakness was shown by their dependence on Britain and France to win the war
1853- American Admiral Matthew Perry docks in a Japanese harbour, the first westerner to do so in centuries; Perry effectively opens Japan up to the world, and starts the ball rolling on Japanese industrialisation
1854- Treaty of Kanagawa signed; limited trade is allowed between the United States and Japan
1855- Alexander II ascends to the throne of Russia; the new Czar is as autocratic as ever, but he's also interested in reform, and would go on to free the serfs
|
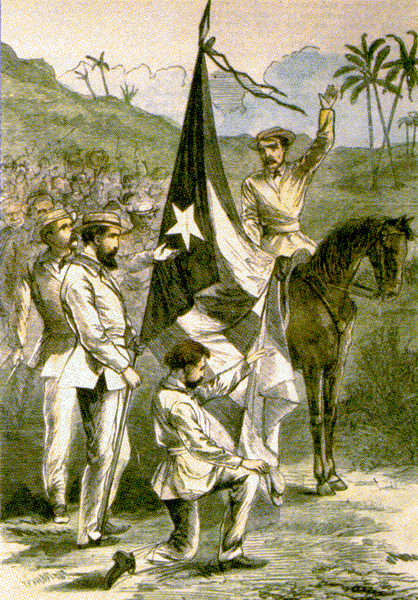
| 7 Years War? Bah! Real Cuban men fight Ten Year Wars! |
1860s- Ten Years' War; Cuba's first struggle for independence, was met with strong Spanish opposition, and was eventually put down; however, its influence would extend well into the next century, inspiring such revolutionaries as Jose Marti, Che Guevara, and Fidel Castro
1861- Serf Emancipation Act implemented in Russia
1861-1865- American Civil War; many southern slave-states secede from the union, creading the Confederate States of America; their reason for this is not just the fact that the northern states would like to abolish slavery altogether, it was also about whether or not to make the newly acquired Western states into slave-holding states or not; the nation is wounded by 5 hard years of in-fighting amongst brethren; finally, the Union, led by Abraham Lincoln as President and Ulysses Grant as general, defeated the confederate south and the slaves were emancipated
1865- As a result of the American Civil War, the United States embarks upon a new plan of acquiring territory reaching as far westward as the pacific coast
1866- Austro-Prussian War; the dispute over the northern German states of Schleswig and Holstein soon exploded into armed conflict; Prussian Chancellor Otto von Bismarck leads Prussia to victory in only 7 weeks
1866- An era of repression begins in Russia, after Czar Alexander II is repeatedly threatened by assassination attempts
1867- The Dominion of Canada is proclaimed, peacefully, with British approval
1867- Due to nationalist pressure from the Hungarians, the empire of Austria becomes a dual monarchy; the empire is now known as Austria-Hungary or Austro-Hungary
1868-1912- The Meiji Era signifies Japan's westernisation, modernisation, militarisation and industrialisation
1869- The Union Pacific Railroad is completed in America, making settling of the west far simpler; the railroad also brings an influx of immigration into North America, both to help build the track and to settle in the western wilderness
|
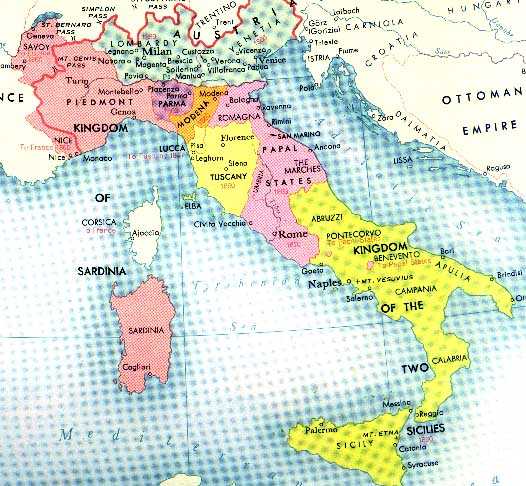
| The living alliterations, Giuseppe Garibaldi & Camillo Cavour, were successful in uniting Italy. |
1870- Franco-Prussian War; Bismarck, who had previously united the northern German states under Prussian influence, started this war by altering a telegram ("The Ems Telegram", sent from the Kaiser to France's Emperor Napoleon III) to make it sound insulting, and thereby causing France to arm for conflict; the purpose of Bismarck's alterations were to scare the southern Germans states into allying with the northern German states (controlled by Bismarck) using the threat of French incursions eastward
1870- After the defeat of Napoleon III at the Battle of Sedan, Prussia had gained control of Germany, and, additionally, the French territory of Alsace-Lorraine; a new German Empire was proclaimed, with Kaiser Wilhelm as Emperor, and Bismarck as appointed Chancellor
1870- With Napoleon III's capture at Sedan, France proclaims its 3rd Republic
1870- In Italy, Piedmont-Sardinian Prime Minister Camillo Cavour's political maneuvering won the Northern States from Austria; in the south, Giuseppe Garibaldi captures the Two Sicilies with an army of just over 1000 men; when the French remove their garrisons at Rome (they need all the manpower they can get when fighting the Prussians), the newly forming Italy takes it as its own; Victor Emmanuel II, King of Sardinia, is proclaimed King of the new, unified Italy

|
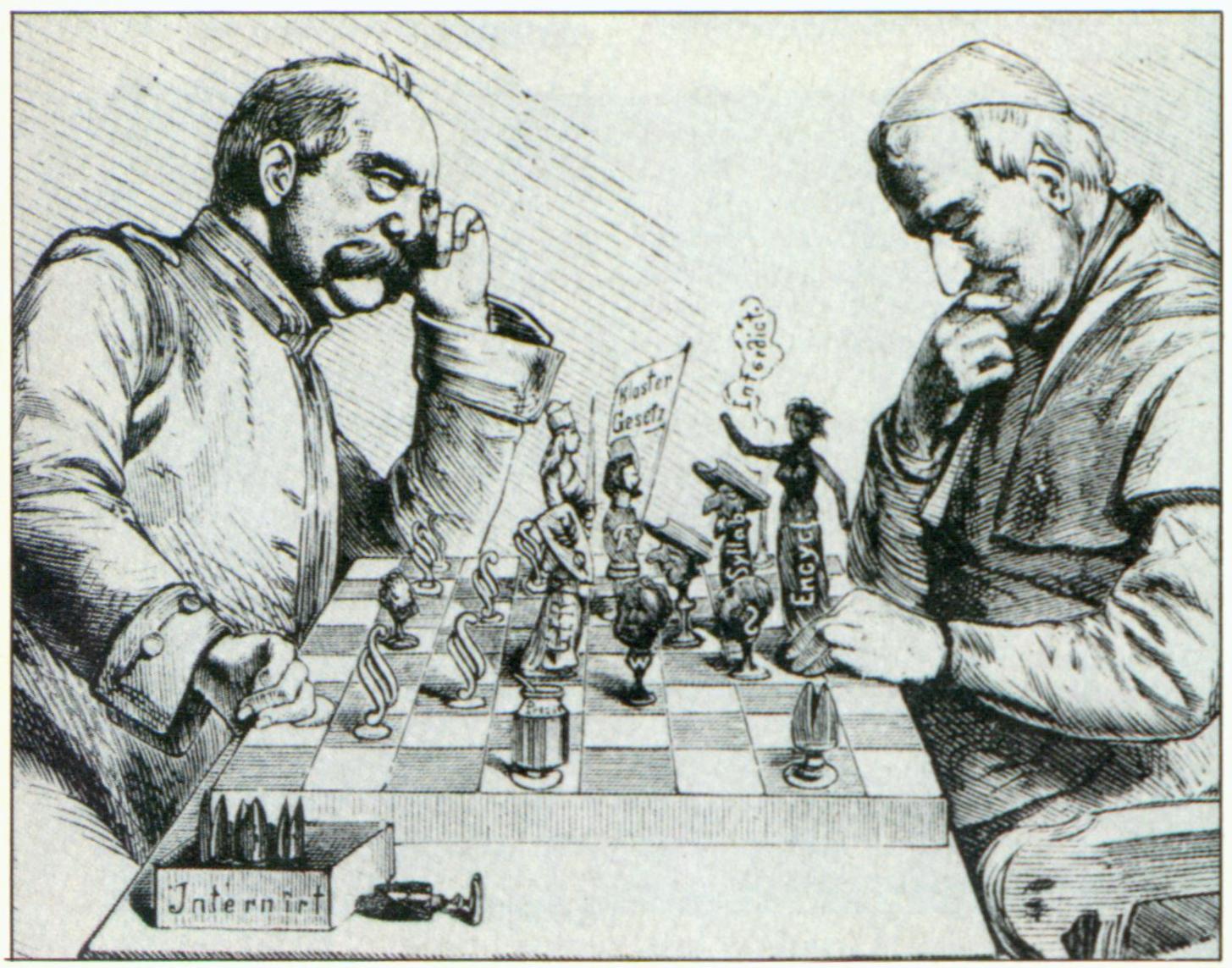
| My money's on the Pope. |
1870s- Kulturkampf; Otto von Bismarck begins a campaign of new, anti-Catholic legislation, greatly damaging relations with the Papacy and the French
1873- The Three Emperor's League is created; Germany, Austria, and Russia become allies
1875- Egypt sells its shares in the Suez Canal to Britain; both Britain and France have joint administration over the waterway, which would prove vital for imperialism and trade
1876- France and Britain gain even more control over Egypt when an Anglo-French consortium takes on the Egyptian debt crisis
1876- International Geographic Congress of Central Africa called by King Leopold II of Belgium; Belgium is granted control of the Congo
1877- The Dutch South African colony of Transvaal (populated by the Dutch farmers, the Boers) is proclaimed a British protectorate; the Zulu Wars are fought just north of the Boer colonies of Transvaal, Orange Free State, and Natal
1878- Congress of Berlin; the major powers discuss the future of the dying Ottoman Empire, and their position on the independence of the Balkan states (Bulgaria, Albania, Rumania)
1879- Dual Alliance formed; Germany and Austro-Hungarian relations become even closer
1880- Egyptian nationalist leader Colonel Arabi El-Wahid leads resistance against foreign (British & French) control
1880- Boer resistance to British administration (i.e. the British outlawed slavery, the Boers wanted to keep their servants working on their farms) grants Transvaal its partial independence
1880s- Major European imperialist movement in the Congo area
1881- Alexander III comes to power in Russia, and the Exceptional Measures Act is passed, allowing use of excessive military force in quelling rebellion in various regions, mostly in east and central Asia
1882- Britain invades Egypt to quell nationalist furor
1882- Italy is added to the Dual Alliance, making it a Triple Alliance, after France invades their North African colony of Tunisia
1883- Tension arises between Belgium and France concerning the colonisation of the Congo region
1884- British General Gordon travels down the Nile to engage the Mahdi (a Sudanese nationalist, freedom fighter), but he and his forces are overwhelmed at Khartoum; the European reaction is one of shock and dismay; the British public asks why General Wolseley's reinforcement armies hadn't arrived quicker, but they receive no answer
1884- Germany begins to intrude in African imperialism
1885- Berlin Congress held, African imperialism discussed among Bismarck and other European leaders
1887- Germany and Russia sign a reinsurance treaty; Russia promises, at least, its neutrality in even of any wars Germany may become a part of, and the Germans pledge to support Russian interests in the Balkans
|
| Bismarck shocked Europe when he announced his interest in colonisation... Then he changed his mind. |
1888- Kaiser Wilhelm II enthroned, clashes with Bismarck
1890- Bismarck resigns as German chancellor
1890- Cecil Rhodes establishes Rhodesia, urging South African pioneers to travel north to settle on the Zambesi River
1894- Nicholas II ascends to the throne in Russia; little does he know that he will be the last of the Romanov dynasty of czars
1894- Japan violently wrests control of Korea away from China in a brief but bloody war; the militarily superior Japanese have the opportunity to destroy the Chinese, but thought better of it; if China was eliminated, then it would be westerners who filled in the large geographical gap in eastern Asia, and the Japanese certainly didn't want that
1894- Dual Entente formed between France and Russia; military agreements made in 1892 are formalized
1894- German military officers adopt the Schlieffen plan
1895- Rhodesia's governor, Dr. Jameson, attacks the Transvaal without British permission
1895- The United States shows its long-lasting support of the Monroe Doctrine when it supports Venezuela in a border dispute with British Guiana over some gold found in a disputed zone; America went so far as to threaten war on Britain, but they backed down once an independent tribunal decided in favour of British Guiana
1895- The Treaty of Shimonoseki; Japan is granted control of the islands of Formosa (Taiwan) and the Pescadores; they also received a 360-million yen indemnity, the rights to travel the Yangtze River, and establish their industries within China
1897- Germany adopts "Weltpolitik", a foreign policy advocating agressive expansion
1898- The Fashoda Crisis- Conflict existed between France and Britain for the control of North Africa; France sent a small group of men eastward up the Niger River, towards the Nile; they arrived at the mud-hut village of Fashoda, and were immediately besieged by Mahdist warriors; the British forces, led by General Kitchener, were fighting the Mahdists on the southern Nile; after a stunning victory at Omdurman, Kitchener levelled the city (and the Mahdi's tomb), then headed west to save the French; the meeting between the two powers was surprisingly cordial, and they agreed to help eachother defeat the Mahdists; the French, realizing that the British could have destroyed them in an all-out war at any time, removed their troops from the East and left Britain to control the Nile
1898- The Spanish-American War- Part 1- After a Cuban revolt in 1895, Spain cracked down on its Carribean colony; many people were imprisoned in inhumane concentration camps, and this angered the American public; President McKinley ordered the Spanish to withdraw from Cuba, for he no longer had no choice in the matter (public opinion was just too strong); Spain responded by declaring war on the United States
1898- The Spanish-American War- Part 2- American ground troops easily overran Spanish forces in Cuba, and Admiral Dewey took Guam and the Phillipines in the Pacific, dismantling the Spanish fleet at harbour in Manila; when the war came to an end, the United States emerged as an imperial power, retaining control over both Puerto Rico and the Phillipines

|
| In the Boer War, the British freed a large amount of slaves (and gold) from Dutch settlers' grasps. |
1899-1902- The Boer War- Part 1- British forces had controlled the Dutch South African farming states of Natal, Transvaal, and Orange Free State for many years, but they still hadn't imposed a British system of rule on the Dutch; the Boers (Dutch farmers) were against any installation of British-style government, for they knew they'd be outvoted in a democracy, and also lose their slaves; the British wanted to implement a federal government in South Africa, including the Boer republics, mostly because of the large amounts of gold and diamonds resting in the area
1899-1902- The Boer War- Part 2- British Secretary of Colonies, Joseph Chamberlain, gave the Boers an ultimatum: accept federation or it will be forced upon you; Chamberlain was ready to fight, and he ordered 47 000 reinforcement from India, Australia, Canada, and the rest of the British empire to show it; the Boers sent back no reply, and attacked before the reinforcements arrived; the surprisingly effective Dutch fighters took the British South African cities of Mafeking, Ladysmith, and Kimberley; then they dug in trenches along the Tugela River
1899-1902- The Boer War- Part 3- Britain brougth in troops from all over its empire, mainly as a show of its strength to the other European powers; war hero General Kitchener was brought in, and the Boer forces fell in February 1900; the British troops spent the next two years wiping out Boer guerilla resisters, sending many to concentration camps; the inhumane camps caused outcry in the British parliament, and were soon abolished
1899-1902- The Boer War- Part 4- In 1902, the last of the Boer commanders surrendered; the Dutch republics were forced into the Union of South Africa, created in 1910, along with the British colonies further south

|
| Sadly, the Allies didn't ACTUALLY fight gorillas in the first World War. |
1902- Japan and Britain sign a mutual alliance treaty
1904-1905- The Russo-Japanese War- The hostile relationship between Russia and Japan exploded into war when the negotiations over the Chinese Yalu timber resources were ended, and Japan performed a shocking surprise attack on Port Arthur; the Japanese enjoyed success due to short supply lines, but they couldn't support a sustained attack on the Russians (who had just too much manpower); the Japanese were able to capture Mukden and Port Arthur, while also destroying both the Russian Pacific Fleet (which was docked in Port Arthur) and the Russian Baltic Fleet (which had sailed halfway around the world to confront Admiral Togo and the Japanese navy); both nations welcome the mediation of American President Teddy Roosevelt in 1905; in the peace treaty, Japan gained control of the Manchurian railway, Korea, and the southern half of Sakhalin island; in a secret treaty in 1907, Russia granted joint power over Manchuria to Japan
1905- Father Gapon, with state approval, marches (with 200 00 workers) on the palace of the Czar to present a petition requesting better working conditions; however, the Czar was away, and the Palace guards panicked when they saw the appraoching mob, and opened fire; 1500 innocent protesters were murdered
1905- October Manifesto- Czar Nicholas II implements a national assembly, the Duma, but he still maintains control of foreign and military affairs; he also has considerable veto powers; the first Dumas were largely ineffective, and favoured the aristocracy; however, the later Dumas instituted successful land reforms, as did Prime Minister Peter Stolypin, who almost led the country into an era of less political disorder; when he was assassinated, Russia returned to its old, unstable ways
1905- The first Moroccan Crisis; tensions rise between Germany and France; Germany dislikes France's wish to control Morocco
1906- The naval race begins between Germany and Britain; both powers attempt to build as many powerful sea vessels as possible
1907- Britain, France, and Russia join together in the Triple Entente, an answer to the Triple Alliance of Italy, Germany, and Austro-Hungary
1908- Austria annexes Bosnia-Herzegovina, raising concern over its dominance in the Balkans
1911- The second Moroccan Crisis; the German warship "Panther" travels to Agadir to support the Moroccans in their fight against French takeover
1912-1913- The Balkan Wars- When Italy invades Tripoli in Northern Africa, the Ottoman Empire is distracted, and the Balkan states seize the opportunity, taking their own independence through war; Russia supported Serbia, and Austro-Hungary supported Bulgaria; Britain and France were concerned that the situation might explode into an all-out war if Russia and Austro-Hungary get involved; luckily, the fighting ended in 1913
1914- Archduke Ferdinand, heir to the Austro-Hungarian throne, is killed by a Serbian assassin; Austro-Hungary threatens Serbia with an ultimatum; shockingly, Serbia accepts Austro-Hungary's terms, but Archduke Franz Joseph is bent on war, and keeps Serbia's response secret; Austro-Hungary invades Serbia, and Russia comes to the small Baltic nation's aid; Germany decides to support the Austro-Hungarians, and they also begin to mount an offensive against the French; the British mobilize their navy, preparing for war
***WORLD WAR 1***
1914- Both Japan and Russia enter WWI on the side of the British and French
1914- Germany invades Belgium; stalemate occurs in France along the Marne River; both sides attempt to outflank eachother in the "Race for the Sea", but neither succeed, and trench lines are dug in; supply stockpiles fail, both sides decide to wait and resupply, and then to continue fighting; an effort at a peace conference fails; meanwhile, on the Russian front, Germany is victorious at the Battles of Tannenburg and the Masurian Lakes; late in the year, the Czar is told that the Russian forces are too weak, and can no longer mount an offensive
1915- in France, a stalemate of bloody trench warfare occurs; the Central Powers destroy the Russian armies; the Allies attempt to attack Germany from the south by landing at Gallipoli, but fail; reluctantly, Italy enters the war on the side of the Allies, in exchange for promised territorial gains after the war; a Middle East campaign is launched by the Allies to defeat the Ottoman Empire, Germany's ally
1916- Battle of Verdun; Germany attempts to take multiple forts at Verdun, the result is dragged on, bloody, dehumanizing violence and warfare; German troops advanced deep into France, before being removed to fight elsewhere
1916- The Somme Offensive; British and French troops attempt to work their way along the Somme River by shelling the German trenches; the Germans retreat back and underground until the shelling ends, and then they retake their positions in machine gun nests, devastating the Allied troops; all in all, the French lose 200 000 men, the British 420 000, and the Germans 450 000
1916- Jutland Naval Battle- The British and German dreadnought forces face eachother in the North Sea; the battle is indecisive, but Britain is able to maintain control of the North Sea
1916- Brusilov Offensive- General Brusilov goes against the Czar's orders to stay in defensive mode, and launches a surprise attack on the Austrian front lines; the Russians plunge 80km deep into enemy territory, only to be massacred by the Germans shortly after; however, Brusilov's actions provided a major distraction, and the Germans were forced to relocate their troops at Verdun to the Eastern Front, aiding the Allied forces in the west
1916- The governments take total control of their countries with the outbreak of complete war; industry works non-stop and women join the workforce in droves
1917- Zimmerman Telegram- Germany offers Mexico valuable American territory when the war is over if Mexico agrees to attack the United States; the telegram sparks American outrage and war becomes a favourable option for President Woodrow Wilson
1917- Germany declares a war zone around Britain; vicious airplane fighting ensues, as air forces come into their own as military entities
1917- The United States enters WWI on the side of the Allies (Russia, Britain, France, Japan)
1917- The Russian Revolution- Due to food shortages, the failing war effort, and worker lockouts, the Romanovs were removed from power and later executed; a provisional government was set up, but it was soon replaced with the Bolshevik communist government, led by Vladimir Lenin, who took power by way of a coup d'etat in 1918; elections were held, and when the Bolsheviks received only 125 seats out of 707, Lenin's army forcefully dissolved the assembly, created a dictatorial single-party government
1918- Brest-Litovsk Peace Treaty signed; by giving heavy concessions to the Germans, Russia was allowed to leave the war and focus on its internal problems
1918- Kaiserschlacht- Germany launches its final western offensive, attempting to find a whole in the allied wall from Ypres to Verdun; they do, and plunge towards Albertville; however, their progress is slowed as soldiers stop in French villages to gorge on wine and food, which they had been denied for so long; this gave the Allies time to recuperate, and, eventually, drive the Germans back
1918- The Last 100 Days- The Allies advance continually; Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicates, and a provisional government is set up in Germany; Armistice is declared- the Allies have won the war
1919- The Treaty of Versailles is signed, confirming Germany's defeat and penance (much of its land and arms are turned over to the Allies); the League of Nations is formed
1919- The American congress refues to ratify the Treaty of Versailles; it declares that hostilities are at an end

|
| When Stalin came to power, he wasted no time Stallin' before cracking down on political opposition. |

|
| In WWII times, much like today, every drop of oil was important. |
1930s- Hitler's National Socialist (Nazi) Party comes to power in Germany; they vow to bring prestige back to Germany, and use the Jewish people as scapegoats
1930s- The Great Depression- Discontent spreads throughout the Western world, as the American stock crash of 1929 affects every aspect of daily life
1939-1945- WWII (*note* WWII will not be gone into with much depth here, due to time constraints; plus, hey, this isn't Social 30!); Germany, Italy, and Japan join together to form the Axis; they battle the Allies, made up of Britain, France, America, and the U.S.S.R.; atrocities are committed both on the battlefield and in the inhuman concentration camps, wherein Nazis tortured and murdered millions of Jews; eventually, destiny favours the Allies, and Germany surrenders on May 7, 1945; after a nuclear strike on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, Japan surrenders on August 15 of the same year; important events following the war include: The Nuremberg Trials, in which Nazi war criminals stood trial, and the occupation of Germany, in which the defeat nation was divided along into East and West Germany, East being Commmunist-controlled, West being Democratic

|
| If India had never escaped British rule, The Beatles may have never met Ravi Shankar! |
1946- On its own Independence Day (July 4), America grants the Phillipines their own freedom and self-government
1947- On August 15, India is officially granted its independence from the British empire
1947- The General Assembly of the United Nations declares the creation of two new Palestinian states: one Israeli and one Arab; on that same day (November 29), Israel is attacked by a coalition of Egyptian, Syrian, Lebanese, and Jordanian forces
1949- Mao Zedong's Communists finally defeat Chiang Kai-shek's Nationalists for control of China; the two factions had been warring almost since the fall of the Emperor decades earlier; Zedong declares the People's Republic of China, with himself as Chairman
1950-53- The Korean War; Communist North Korea makes incursions on the territory of Democratic South Korea; the conflict grows to involve two major powers in the world: China enters on the side of the North Koreans, and America intervenes on behalf of the South Koreans
1958- China attempts to modernize; "The Great Leap Forward"; the program would result in hunger and poverty; it was a total failure
1960s- A new era of anti-governmentalism begins in the United States; rallies and protests become more frequent, a harsh change from the rigid patriotism of the '50s
1965- Chairman Mao institutes the Cultural Revolution in China; thousands of communist youth soldiers ('Red Guards') take control of local governments and terrorize the population
late 1960s-early 1970s- The situation in Vietnam, once again a conflict between communism and western democracy, simmers into a war; the United States becomes heavily involved, and drafts many young people into the armed forces; the entire war is a disaster and a loss for the Americans, as they are forced to retreat among accusations of scandal, while the communists remained in power in Southeastern Asia
1971- The U.N. permits the People's Republic to represent China instead of Taiwan
1972- American President Richard Nixon visits China and is met by Mao's right hand man, Chou En-lai, at the airport; relations between the two superpowers improve
1974- U.S. President Richard Nixon resigns amid accusations of corruption in the Watergate affair (Nixon's aides were caught burglarizing and wire-tapping the Democratic headquarters in the Watergate Apartments); the average American's faith in the government is severely damaged
1984- Britain and China agree to the terms of Hong Kong's return to Chinese rule after being a British colony for about 100 years; it is one of the last remaining reminders of European colonisation of the Chinese coast
1989- Tiananmen Square Massacre; thousands of protesters are killed or injured in China when the army cracks down; the crowds were made up mostly of students clamoring for more democratic freedoms

|
| Evil, thy name is Jorg. |
1989- Berlin Wall falls; East and West Germany are reunited after 40 years of seperation
1989-91- The breakup of the U.S.S.R. heralds a new era of European and Asian nationalism as scores of new republics appear across the map; Ukraine, Kazakstan, Uzbekistan, and Azerbaijan, to name a few, enjoy newfound freedoms
1990s- Yugoslavia slowly breaks up, first Slovenia leaves, then Croatia and Bosnia-Herzegovina, and, finally, with the fall of the tyrant Slobodan Milocevic, mostly all of the people of the Balkans are free to self-govern as they please
2000s- A resurgence of nationalism occurs in Europe; the nationalist feelings are usually anchored in neo-fascit or anti-immigration platforms; examples include the late Pim Fortuyn of Holland, and Jorg Haider in Austria
The Future- Who knows what the future holds for a concept as powerful and chameleon-esque as nationalism? No one, that's who. |
